In water management, Water quality monitoring is an important process concerning pollution control. In the process of evaluation, removal of organic matters is a very important aspect. Treatment efficiency in a wastewater treatment plant (WWTP) is evaluated based on effective removal of biodegradable organic substances. In environmental analysis, BOD & COD are such parameters to be measured. The amount of BOD and COD present in waste-water depends on the availability of organic matter in water which includes plant decay and leaf fall, urban runoffs bringing in pet waste, nutrients from lawn fertilizers, paper from residential areas- all contribute to the increased oxygen demand. The conventional method sample collection & offline testing of BOD determination is ineffective as it takes around 5 or 7 days ,which is not the true result & corrective action would be delayed.
So there is a definite need to monitor BOD and COD in real time continuously in wastewater.
Let us discuss the importance of monitoring BOD and COD in this article.
BOD :
Biological oxygen demand (BOD) is the quantity of oxygen consumed by the aerobic bacteria used in the oxidation of organic matter. It is a measure of the degree of contamination of water and it is expressed in mgO2/L.
COD :
Chemical Oxygen Demand is a measure of oxygen utilized to chemically oxidize the organic matter & produce inorganic end products & is used to assess the effect of discharged wastewater in the environment. Reduction in the availability of dissolved oxygen happens when there is higher COD levels. 50 – 2,000 mgO2/L is the industrial water range, although it may reach 5,000, depending on the type of industry.
Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) and Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) are two of the most important parameters to characterize (measure the degree of pollution) of wastewater. The COD measures all the organic matters whereas BOD only measures organic matter which is biologically degraded. Therefore, the COD is always greater than the BOD.
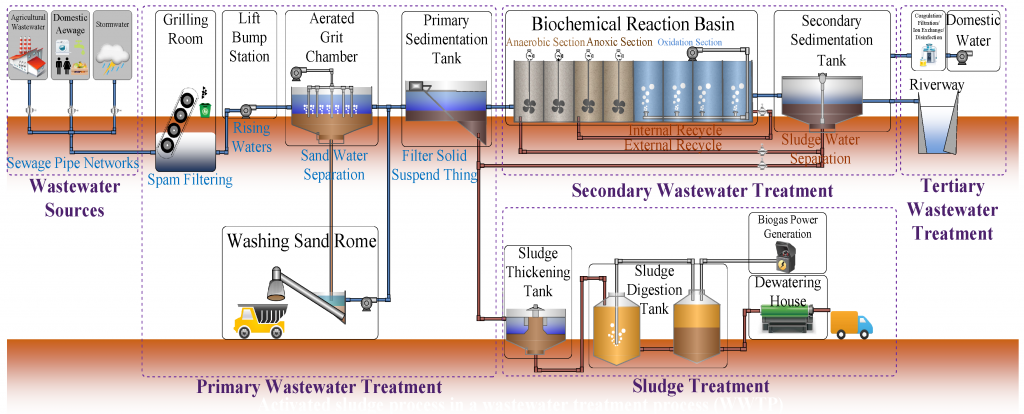
Wastewater Treatment :

In untreated wastewater, the availability of organic carbon is relatively abundant and has become a critical concern for operators of Water Resource Recovery Facilities (WRRF). The dissolved oxygen is used to consume organic carbon in treated wastewater. Water for aquatic species & for recreational & community use will be threatened , when the concentration of organic carbon in treated wastewater is too high.
Environmental Impact :

Oxygen demand plays an important role in aquatic life. The aquatic ecosystem has a cycle which comprises taking up inorganic nutrients to produce organic tissue by algae and other producers in the water. Consumers like fish and other aquatic animals eat some of the producers, These algae are consumed by fishes and the nutrients move up the food chain. After the death of fishes and aquatic animals they are decomposed by bacteria and released inorganic nutrients such as nitrate, phosphate, calcium, and others.
As bacteria are aerobic in nature, it will create oxygen demand for the existing aquatic organisms as it robs other aquatic organisms of the oxygen they need to live. The aerobic bacterial activity leads to a decrease in the natural levels of oxygen in aquatic systems. 5 parts per million (ppm) is the ideal dissolved oxygen concentration for aquatic life.
The dissolved oxygen demand drops drastically when abnormally high levels of aerobic bacterial activity take place. This occurs due to the sudden abnormal pollution introduced into the water body from the sources such as septic tank leakage, domestic sewage, and fertilizer runoff.
Benefits of Monitoring BOD and COD :
- The performance of the clarifier can be improved.
- Sludge quality can be increased.
- Industrial discharge events detected safely.
- Decrease the handling cost
Water Quality predicted based on BOD level :
- Pure water: 2 – 20 mg/L
- Slightly polluted water : 20 – 100 mg/L
- Moderately polluted water: 100 – 500 mg/L
- Highly polluted water : 500 – 3,000 mg/L
Conclusion
Thus it is very important to monitor the BOD and COD in wastewater in order to prevent environmental pollution and it becomes a life saving measure for aquatic animals and fishes. RLT provides BOD and COD analysers with advanced technology and is capable of providing accurate data in real time.
Hope you find this blog useful and informative. Let me know what you think in the comment section below
“Get in touch with us today to learn more about our products and services”. Let’s help you prevent pollution & add value to global sustainability!.
FAQ’S
1.What is BOD?
Biological oxygen demand (BOD) is the quantity of oxygen consumed by the aerobic bacteria used in the oxidation of organic matter.
2.What is COD?
Chemical Oxygen Demand is a measure of oxygen utilized to chemically oxidize the organic matter used to assess the effect of discharged wastewater in the environment.
3.What is the safest level of DO for aquatic life?
5 parts per million (ppm) is the ideal dissolved oxygen concentration for aquatic life.
4.What is a clarifier?
In the metal tank used in the process of sedimentation of waste from water.
5.What is WWTP?
Wastewater Treatment Plant is man made infrastructure involved in treating the wastewater.



BOD test is notoriously imprecise, but it accurately measures (though indirectly) the amount of organic material available to the microorganisms.
COD uses strong oxidants to oxidize the organic matter and the assumption is that all of the organics will be destroyed.
Therefore for Municipal wastewater BOD, N, P, SS, Pathogens, Trace or persistent organics measurements are more necessary. COD in such case may not be required. Ofcourse if one still wants to utilize COD, then TOC as well can be utilised.
Your style is so unique in comparison to other people
I have read stuff from. Thanks for posting when you’ve got
the opportunity, Guess I’ll just bookmark this blog.